
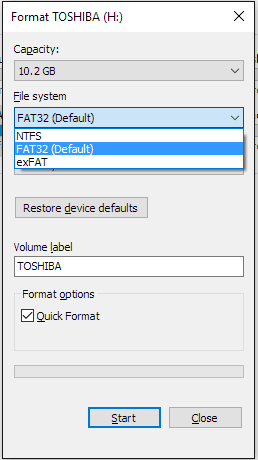
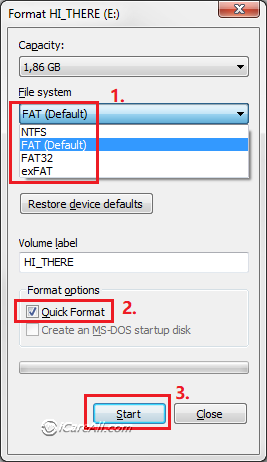

The truth is that FAT32 has a theoretical volume size limit of 16 TB, with a current practical limit of about 8 TB-plenty for most USB drives. Run Command Prompt to format FAT32 Compared with other methods, the Diskpart command may be a little complex. Specifications put out by manufacturers on file systems as they pertain to drive size created the myth that FAT32 can only be used to format drives between 2 GB and 32 GB, and that is likely why native tools on Windows-and other systems-have that limit. Every major operating system and most devices support it, making it great for drives you need to access from different systems. The advantage to using FAT32 is portability. If you do need those larger file sizes, you’ll need to stick with something like NTFS or exFAT. RELATED: What File System Should I Use for My USB Drive?įAT32 is a solid file system for external drives, so long as you don’t plan to use files over 4GB in size. On a Mac, open Disk Utility, then click your SD card > Erase > Format > MS-DOS (FAT) > Erase The Basics of Formatting You can format most SD cards to FAT32. Swap "X:" for the drive letter assigned to your USB drive.įor whatever reason, the option to format USB drives larger than 32GB with the FAT32 file system isn’t present in the regular Windows format tool. This can be done by using COMMAND + SPACE (which launches Spotlight so that we can search for the app) and then type in ‘Terminal without quotations. Alternatively, launch PowerShell as an Administrator and run "format /FS:FAT32 X:" in the Window to format the "X:" drive as FAT32. Connect the USB drive that you want to format to FAT32 to your Mac. Use a third-party utility, like "FAT32 Format," to format larger USB drives with FAT32.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
